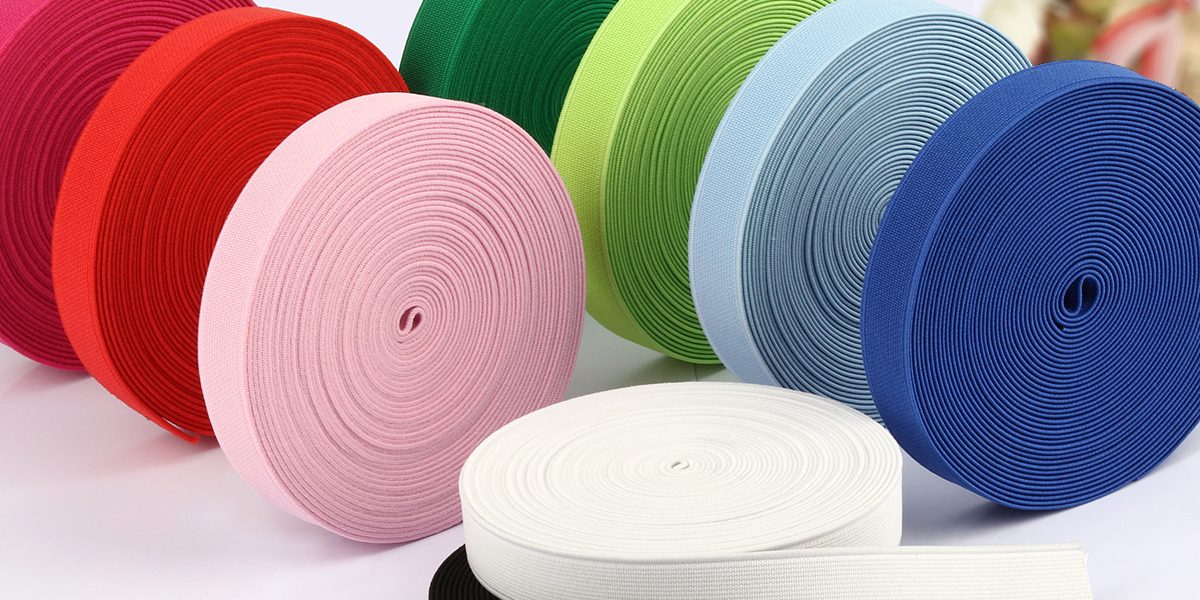
Elastic webbing’s remarkable properties are rooted in the science of materials engineering. In this blog, we will explore the scientific principles that underlie the elasticity of webbing.
Elastic webbing is typically made from synthetic materials such as polyester, nylon, or latex rubber. These materials are chosen for their elasticity and durability.
The molecular arrangement of the elastic fibers within the webbing allows it to stretch and return to its original form. This structure provides the material with its unique properties.
Elasticity refers to a material’s ability to deform when subjected to stress and then return to its original shape when the stress is removed. Elastic webbing exhibits this property, in contrast to materials that exhibit plasticity and remain deformed.
Elastic webbing is engineered to have high tensile strength, allowing it to withstand significant loads while maintaining its elasticity. This combination of flexibility and strength makes it invaluable in a wide range of applications.
By understanding the science behind elastic webbing, manufacturers can continue to innovate and develop new products that harness its unique properties for various industries.